Lymphedema
Lymphedema
OVERVIEW
Lymphedema
Lymphedema/elephantiasis is progressive disease where there is increase in size of limbs or body part, if untreated results in complications like wounds, water discharge or immobility/ poor quality of life.
Sakra world hospital conducts a Special Clinic for lymphedema.
Sakra world hospital is one of few centers giving complete care and treatment of lymphedema in India with all modern state of art facility. Dr Rajendra S Gujjalanavar is trained in supermicrosugery and treating these cases from many years.

What are the causes of lymphedema?
Primary lymphedema is due to developmental abnormality of the lymphatic system. They are of three types:
- Congenital lymphedema is clinically evident at birth and accounts for 10% to 30% of all primary lymphedemas.
- Lymphedema praecox is the most common form of primary lymphedema, presentation at puberty is the most common and females are affected four times as frequently as males.
- Lymphedema tarda is a primary form of lymphedema that manifests clinically after the age of 35 years, occurs more commonly in women.
- Traumatic lymphedema occurs as a consequence of scarring or injury following trauma, cancer surgery (breast and gynecological cancer), burn injury, or radiation exposure. It also can occur after extensive skin resection.
- Infective lymphedema is caused by invasion by organism and subsequent destruction of the lymphatic vessels. This is usually the filarial worm. But is also related to tuberculosis bacteria or other infective bacteria and fungi.
- Malignant lymphedema is caused as a result of infiltration by malignant cells and subsequent obstruction of the lymphatic system.
What are the symptoms of lymphedema?
- Limb swelling
- Tightness in the skin
- limb Heaviness , fatigue, and difficulty moving a joint
- Recurrent infections
- Limited movement of affected area
- Hardening or thickening of the skin(fibrosis)
How is lymphedema diagnosed?
- Limb swelling
- Tightness in the skin
- limb Heaviness , fatigue, and difficulty moving a joint
- Recurrent infections
- Limited movement of affected area
- Hardening or thickening of the skin(fibrosis)
How is lymphedema diagnosed?
This condition is diagnosed by:
- Physical examination and history
- Imaging
- Lymphoscintigraphy
- Indocyanine green dye scan
- MRI
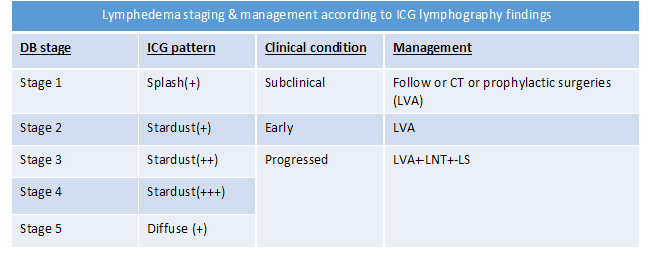
What is the staging of lymphedema?
Treatment depends on the stage of the lymphedema
how lymphedema treated?
- Earlier intervention is new focus of lymphedema management.
- Surgery should be offered early in the course of disease to be effective as conservative treatment never been proven to prevent progression.
- Conservative treatments should be offered in conjunction with surgical treatment.
Non-surgical treatment:
- Complex decongestive therapy (CDT) is aims to decrease the amount of fluid in lymphedematous tissues. CDT is comprised of multiple therapies that include manual lymphatic drainage (MLD), skin care, compression wraps with short-stretch bandages, and lightweight exercises.
- Compression therapy includes multilayer bandaging, self-adherent wraps, and custom-made pressure garments.
- Intermittent pneumatic compression.
Surgical treatment:
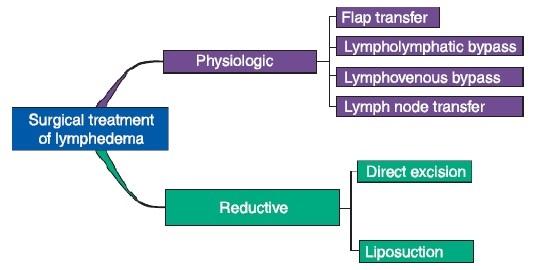
1. Lymph venous anastomosis or bypass (LVA)
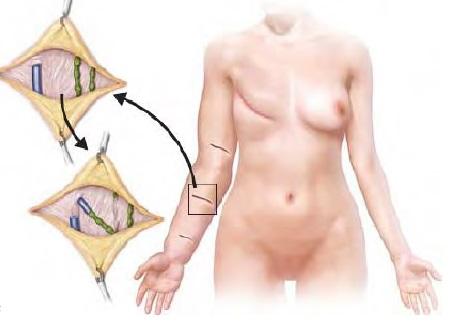
The lymphatic vessels (green) are anastomosed to the veins (blue) at multiple sites. This is supermicrosugical procedure.
In this surgery, vein and lymphatic mapping done before the begging of surgery, based on this imaging small cuts are made at multiple site at affected area and LVA done. It is day care procedure and patient can resume their daily activities from same day and can resume all activities in one-week time. Compression garments need to be worn for 6 months after surgery. Results of the surgeries are appreciated by 3 to 6 months after surgery
2.Vascularized Lymph node transfer(VLNT):
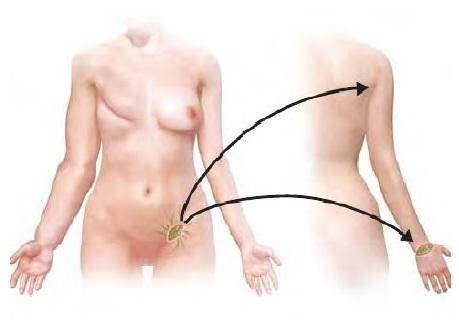
Lymph nodes from the neck ,axilla, groin or from abdomen(omental) is transferred to the affected limb.
This procedure is done under general anesthesia and needs 3 to 4 days’ admission. Patient can resume their daily activities by one week and heavy duties by 3 to 4 weeks after surgery. Patient need to wear compression garments for 6 months to one year following surgery. Results of the surgery are usually appreciated by one-year time and this will improve over next few years.
3. Lymphedema reduction surgeries:
These are done in advanced disease with severe skin changes
- Liposuction- excess fat is sucked out from affected limb through the keyholes by specializes liposuction machine.
- Sistruck procedure – In this the limb size is reduced by debulking and primarily suturing
- Charles procedure where in the involved affected skin is excised up to the fascia and grafting with healthy skin is performed
A combination of the above surgical procedures may be required in multiple stage for Best Treatment for Lymphedema of the patient depending on the presentation and response to the initial treatment.
Prophylactic/preventive Surgery for lymphedema
Lymphedema is progressive in nature, and its management is quiet challenging. Once developed lymphedema is very difficult to cure, and preventive approaches are important to reduce burden on public health. There are two ways of lymphedema prevention;
- Primary prevention-preventive intervention is performed simultaneously in cancer surgery includes reverse mapping, LVA.
- Secondary prevention- Minimally invasive preventive surgery is performed for cancer survivours with high risk of lymphedema development.
There are 2 minimally invasive surgical preventive approaches
a) Efferent lymphatic vessel to venous anastomosis (ELVA)
b) Minimally invasive lymphatic supermicrosurgery (MILS)
What are the risks?
Infection, bleeding, delayed healing, partial/delayed/no recovery.
How will be the recovery after procedure?
Effects of lymphedema surgery especially physiological procedures takes time to show results, anywhere around one year. During this phase patient has to follow strict protocols regarding to wearing compression garments, foot/limb care, exercise, foot end elevation.
