Craniosynostosis
Craniosynostosis
Craniofacial surgery deals with correction and reconstruction of congenital and acquired defects of head, skull, face, jaw and associated structures.
Treatment requires multidisciplinary management with involvement of plastic surgeon/Craniofacial surgeon, Neurosurgeon, Paediatric anesthetist and intensivist, Ophthalmologist, ENT surgeon, Speech therapist, Orthodontist etc.
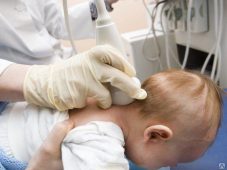
Sakra World Hospital is that the only hospital in India to supply Minimally Invasive Endoscopic assisted surgery and 3D printed helmet therapy for such children Dr Rajendra S Gujjalanavar is specially trained in management of craniosynostosis Craniosynostosis is a birth defect during which one or more of the sutures in an infant (very young) skull fuses prematurely by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull.
How craniosynostosis effects skull?
Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture of skull, it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the fused sutures. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the required space for the growing brain, but leads to an abnormal head shape and abnormal features of face.
In cases during which the compensation doesn’t provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, eating difficulties, sleeping impairment, or an impairment of mental development combined with a big reduction in IQ.
Types of Craniosynostosis
- Non syndromic craniosynostosis – Metopic, Coronal, , Sagittal, Lambdoid, Multisuture.
- Syndromic craniosynostosis – Craniosynostosis occurs as a part of syndrome, Apert, Pfeiffer, Crouzon, Muenke, SaethreChotzen.
Presentations of various craniosynostosis
Unicoronal craniosynostosis it occurs when one of the coronal sutures fuses before birth, causes flattened forehead and raised eye socket one side (Plagiocephaly). The coronal sutures run from the anterior fontanelle right down to the side of the forehead.
Bicoronal craniosynostosis It occurs when both coronal sutures fuse before birth causes head to be wider and to become flattened from front to back (Brachycephaly). The coronal sutures run from the anterior fontanelle right down to the side of the forehead.
Metopic craniosynostosis It occurs when metopic sutures fuse before birth causes head to be a triangle shape (Trigonocephaly).Metopic suture runs in front of skull bone.
Sagittal craniosynostosis It occurs when sagittal sutures fuse before birth causes head to become narrower and longer (Scaphocephaly).sagittal suture runs in center of skull.
Lambdoid craniosynostosis it occurs when one of the lambdoid sutures at the back of the head fuses before birth causes head to be flat at back (posterior plagiocephaly or brachiocephaly)
Multisuture Synostosis in this many or all sutures of the skull close prematurely, cause head to be small(Microcephaly) and severe
restriction of brain growth.
Diagnosis
Is by clinical examination assisted with skull xray, 3D CT scan of head and MRI (sometime) to assess the brain.
Treatment of craniosynostosis
Treatment requires multidisciplinary management with involvement of plastic surgeon, Neurosurgeon, Neuroanaesthetist and intensivist, Ophthalmologist, Speech therapist, Orthodontist etc. The treatment for craniosynostosis is surgery. The type of surgery depends on the sort of the disease and therefore the age of the kid .
Non syndromic single suture craniosynostosis
Age less than 6 months
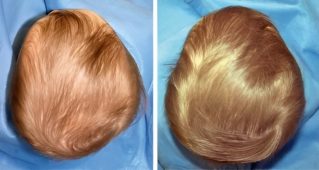
Minimally invasive (Keyhole), endoscopic assisted strip craniectomy followed by Helmet (3D printed) therapy for 1-2 years. In this the fused suture in question is removed using a keyhole incision with minimally invasive techniques. It involves shorter hospital stay, minimal blood loss, avoidance of blood transfusion and quick recovery. This is followed by 1-2 years of helmet therapy to mould the shape of the skull and facilitate proper growth of the brain.
Age more than 6 months
An open surgery (Fronto-orbital remodeling or cranial vault remodeling) is performed for reshaping the skull of the child. The cut is made at the top of the head from one ear to the other ear. The affected suture is removed by a neurosurgeon and the bones of the skull are moulded into normal shape by a craniofacial plastic surgeon.
Syndromic craniosynostosis
Posterior vault expansion/Fronto-orbital advancement
An open procedure to increase the size of the skull to give more space for the brain to grow. This is usually done in the first year of life. Multiple surgeries are often required in syndromic craniosynostosis and the timing of these surgeries depend upon the condition of the child. Lefort III osteotomy and advancement after age 4 is sometimes required to improve obstructive sleep apnoea and airway issues. Extra support for your child is sometimes required. They are – Physical therapy, Occupational therapy, Speech-language therapy, Special education.
What happens in the keyhole skull expansion surgery?
Your child will be properly assessed before surgery by a paediatric neuro anesthetist. An eye check will also be performed. The surgery takes 1-2 hours and is done under general anesthesia. Because it involves just a small cut in the scalp, there are no major scars, no major blood loss. Your child will stay in the ICU overnight. Your child may require blood transfusion occasionally. The pain will be controlled very well in the ICU by our critical care specialists. We encourage normal feeding during the recovery period. Your child will be shifted to the normal ward the next day. You can expect to be discharged from the hospital after removal of the head dressing on the 3rd day usually. You will be able to give normal head shower to the baby after that.
What happens after discharge?
After a post-operative check at 1 week, Helmet therapy is usually commenced with our Orthotic partners (KARE or Osteo3D). This will continue for 1-2 years until a nice head shape is achieved. We might have to change the helmet once or twice depending upon the progress. You will meet the Craniofacial surgeon and Neurosurgeon in regular intervals for monitoring.
What happens in an open Fronto orbital advancement surgery?
Pre-operative assessment done by a paediatric neuroanaesthetist and ophthalmologist. The surgery is done under general anesthesia and usually takes 4-5 hours. Almost all the children need a blood transfusion during and after the surgery. There will be a cut made from one ear to the other to gain access to the skull. The neurosurgeon protects the brain, while the plastic surgeon/craniofacial surgeon does reshaping of the forehead bones. Bones are usually fixed with absorbable plates and screws and sometimes with Stainless steel wires or stitches. The wound will be closed with absorbable stitches. There will be a head bandage. Your child will spend the first night in the ICU and subsequently be shifted to the ward. You will notice significant swelling of the head and face and the eyes may close over for 3-4 days. The swelling gradually reduces over the week. Your child will be discharged usually on the 6th or the 7th day after removal of head bandage. You will be able to give head shower to the baby after that.
What happens after discharge?
You will have follow up visits with the plastic/craniofacial surgeon and neurosurgeon periodically. This is usually a onetime procedure, and if there is no associated syndrome, that’s all your child will ever need. There is no need for Helmet therapy after open remodeling procedure. You will notice some gaps in the skull which will close over in 2-3 years’ time. The scar also is usually well hidden in the hair.
What complications can I expect?
This is a major surgery and you need to be well informed about all complications. Infection, bleeding, scar, swelling and pain are common complications that can happen. All these can be managed by medications. Minor tears in the covering of the brain is sometimes seen which is usually repaired during the surgery. Very rarely there might be injury to the eye or the brain.
Craniosynostosis Categories
Related

Cleft lip and Palate
Cleft lip and palate is condition where their Openings or splits within the lip and roof of the mouth. These are common birth conditions occur alone or as a part of a genetic condition or syndrome.
READ MORE
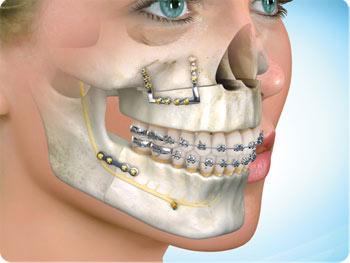
Maxillofacial Surgery
Facial trauma or maxillofacial trauma, is physical trauma to the face. Facial trauma can involve soft tissue injuries such as burns, lacerations bruises and eye lid injury, or fractures of the facial bones.
READ MORE
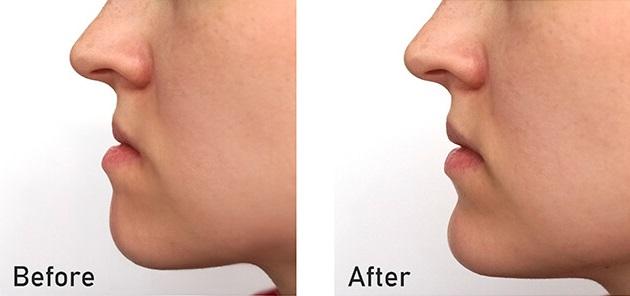
Orthognathic surgery/Jaw surgery
Orthognathic surgery also referred to as corrective jaw surgery or just jaw surgery, is surgery designed to correct conditions of the jaw and face associated with structure.
READ MORE